The iPhone 13 Pro and the iPhone 13 Pro Max is the most technologically advanced smartphone that Apple ever make to date. The technologies that is packed in the Pro lines are class leading and in some cases, ahead of the competition. That being said, let’s not discount the “base” iPhone models. While Apple does not release sales figure by model types, but it is safe to assume that being at the lower price point than the Pro models, it’s a sales leader in Apple’s line up.
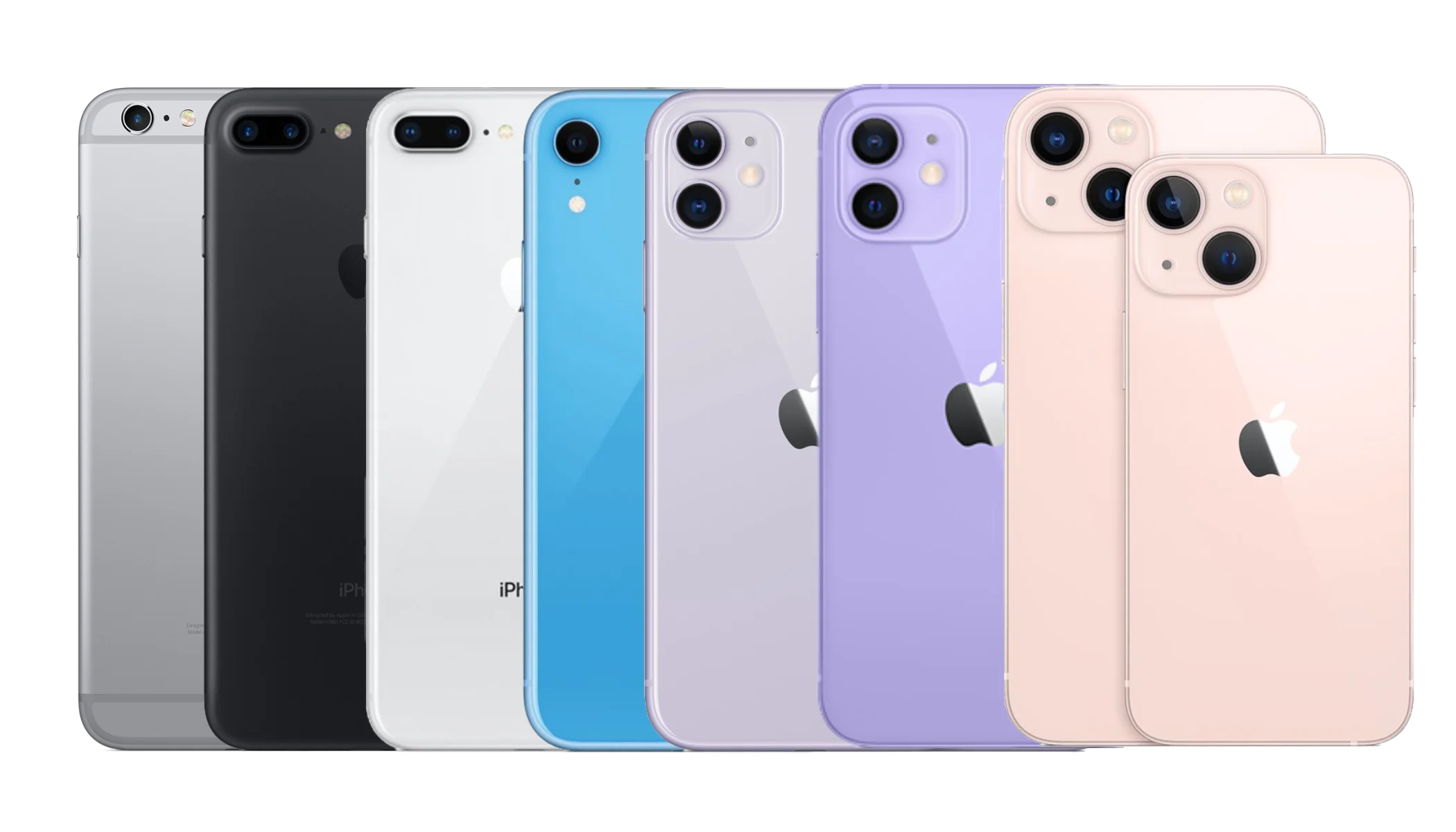
While the Pro models gets the press coverage due to it’s halo features, let’s not forget the evolution and improvements over the generations of “base” iPhone to see how far the iPhone has come. See how far the “common” tech of the iPhone reach to its over billion user base. We will do a generational comparison from iPhone 6s (amazingly still supported by Apple over iOS updates) to the latest iPhone 13.

The Chip
The secret sauce of the iPhone is the system on chip (SOC) that powers the iPhone and Apple A-series chip is class leading example of human ingenuity in building nano-sized circuits that essentially powers the mordern world. In this case, the generational leap has been impressive. From 2 billion transistors in the A9 that powers that iPhone 6s Plus to over 15 billion in the A15 on the iPhone 13. What’s more impressive is how much the transistor density has grown over the years from 20 million per millimeter square in the A9 to the almost 135 million in the A14. What the translates into is that more work is capable to be done while using the same amount of power.

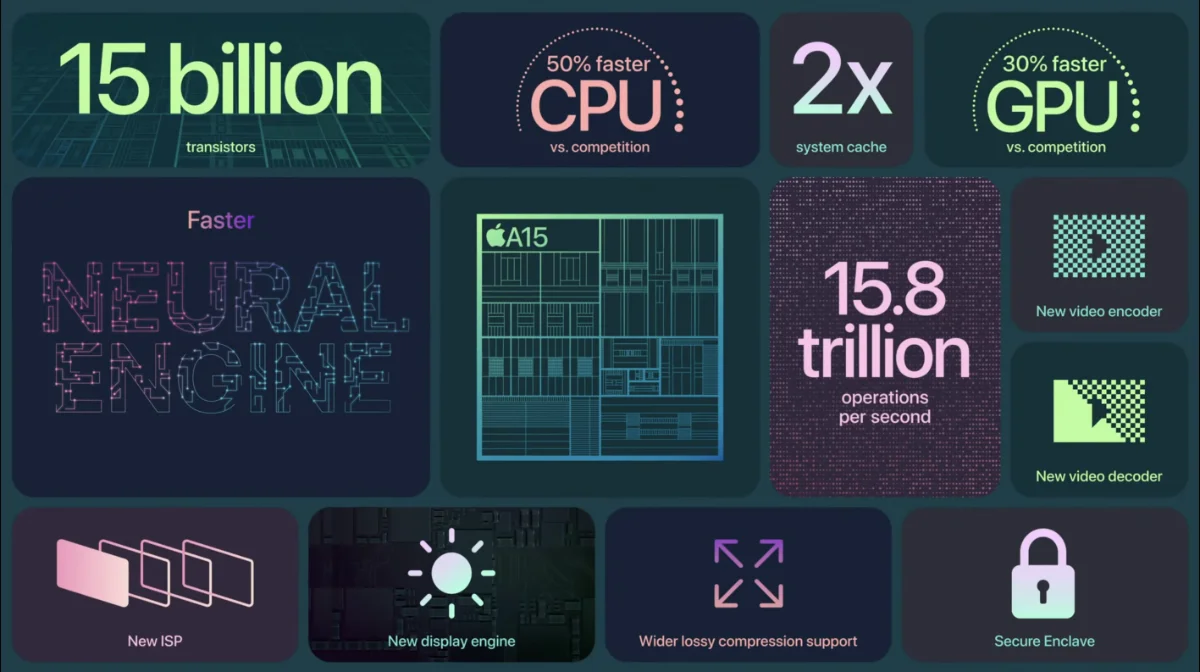
| Feature | A9 | A10 Fusion | A11 Bionic | A12 Bionic | A13 Bionic | A14 Bionic | A15 Bionic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Introduced (iPhone) | 2015 (iPhone 6s) | 2016 (iPhone 7) | 2017 (iPhone 8) | 2018 (iPhone Xr) | 2019 (iPhone 11) | 2020 (iPhone 12) | 2021 (iPhone 13) |
| Transistor Count (billions) | 2 | 3.3 | 4.3 | 6.9 | 8.5 | 11.8 | 15 |
| Production Process | 16nm to 14nm | 16nm | 10nm | 7nm | 7nm | 5nm | 5nm |
| Estimated Die Size (mm^2) | 104.5 | 125 | 87.66 | 83.27 | 98.48 | 88 | ? |
| Estimated transistor density (million / mm^2) | 19.13 | 26.4 | 49 | 82.87 | 86.32 | 134.90 | |
| Compute Cores | 2x 1.85 Ghz | 4x 2.34 Ghz | 6x 2.34 Ghz | 2x 2.49 Ghz and 4x 1.6 Ghz | 2x 2.65 Ghz and 4x 1.8 Ghz | 2x 3.1 Ghz and 4x 1.8 Ghz | 2x 3.22 Ghz and 4x ?? Ghz |
| Graphic Cores | PowerVR 6-cores | PowerVR 6-cores | Apple 3-cores | Apple 4-cores | Apple 4-cores | Apple 4-cores | Apple 4 or 5 cores |
| Neural Cores | - | - | 2-cores | 8-cores | 8-cores | 16-cores | 16-cores |
| GeekBench 5 (single-core) | 558 | 776 | 932 | 1118 | 1334 | 1592 | 1726 |
| GeekBench 5 (multi-core) | 1024 | 1422 | 2569 | 2764 | 3524 | 4112 | 4606 |


The Screen
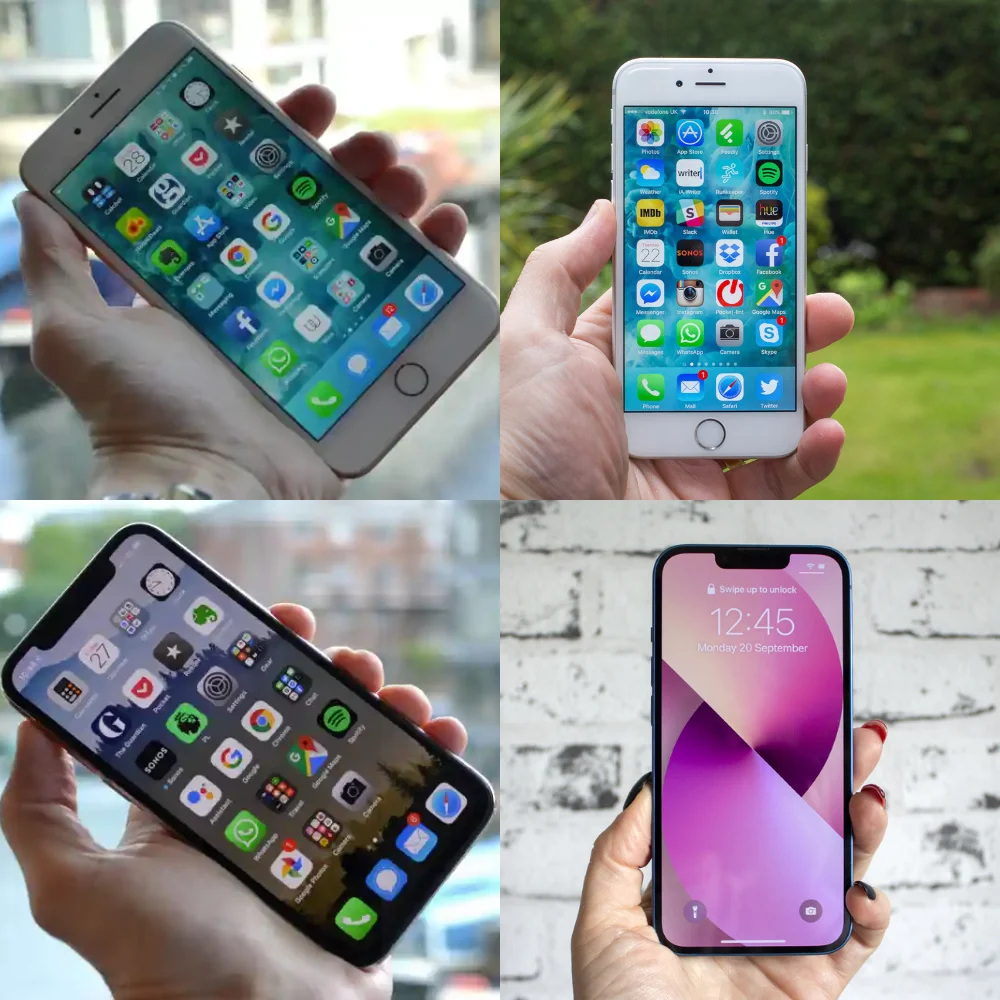

The screen size does not change much over the years because unlike a television, you can use only have so much space in your pocket or in your messenger bag. However, the technology in displaying your content on the screen gets better and better. First, the color representation gets better because the gamut runs from sRBG to P3. Then, it has True Tone function where it can change the white balance of the screen to match your ambient light.

The big leap was when the screen changed from LCD to OLED, where instead of having a back light to show the content, each of the pixel is bright enough to show the actual content. This means that is dark will stay dark instead of a dark grey. You can now see content in a higher dynamic range (a bigger difference between dark objects and a light object) to closer match real life. And of course the screen goes brighter after each generational change.
| Feature | iPhone 6s Plus | iPhone 7 Plus | iPhone 8 Plus | iPhone Xr | iPhone 11 | iPhone 12 | iPhone 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screen Tech | LCD | OLED | |||||
| Screen Size (inches) | 5.5 | 6.1 | |||||
| Resolution | 1920 x 1080 | 1792 x 828 | 2532 x 1170 | ||||
| Typical Brightness | 500 | 625 | 800 | ||||
| HDR Brightness | - | 1200 | |||||
| True Tone? | No | Yes | |||||
| Gamut | sRGB | P3 | |||||
The Camera
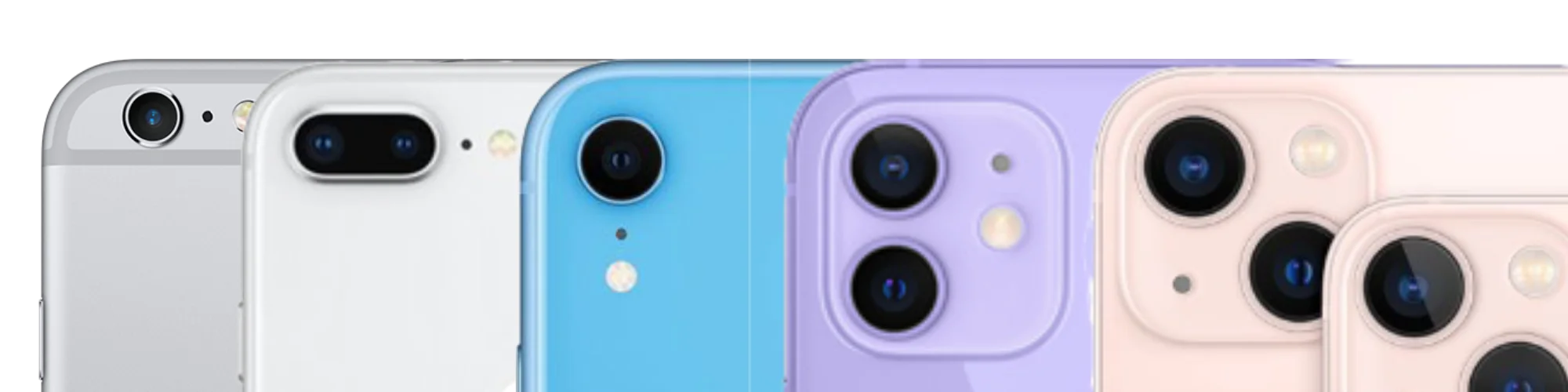

Next to the screen, the camera is the next single most important feature of any smartphone, and the iPhone has been consistently excellent in this area for each generation. Now, with the iPhone 13, we now no longer have a smartphone that can take pictures, but a camera that can take calls. iPhone and their Android counterpart has single handedly killed the point and shoot market.
For each generation, Apple make the camera bigger, a larger camera hump (you still can’t cheat physics), the sensor more sensitive and a the neural engine more powerful so it will have more clever camera tricks like changing the render, potrait mode (artifically blurring the background to mimic a larger sensor), night mode (enhancing night photos), night sky mode (easier to take pictures of stars at night) and now photographic styles (auto adjust the style settings) and cinematic mode (adjust the focus intelligently by detecting faces.)
So the biggest improvement that the iPhone 13 has over previous generation is the improvement of the camera sensor and function.
| Feature | iPhone 6s Plus | iPhone 7 Plus | iPhone 8 Plus | iPhone Xr | iPhone 11 | iPhone 12 | iPhone 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||||||
| Ultrawide Lens | - | 12 MP, f/2.4, 13mm | |||||
| Wide Lens | 12 MP, f/2.2, 29mm, 1.22 micrometer | 12 MP, f/1.8, 28mm | 12 MP, f/1.8, 26mm, 1.4 micrometer | 12 MP, f/1.6 26mm, 1.6 micrometer | 12 MP, f/1.6 26mm, 1.7 micrometer | ||
| Telephoto | - | 12 MP, f/2.8, 56mm | 12 MP, f/2.8, 57mm | - | |||
| Selfie | 5MP, f/2.2, 31mm | 7MP, f/2.2, 32mm | 12 MP, f/2.2, 23mm | ||||
| Photo capabilities | |||||||
| Night Mode | - | Yes | |||||
| Portrait Mode | - | Yes | |||||
| Photographic Styles | - | Yes | |||||
| Video capabilities | |||||||
| Slow-Mo | Up to 240fps @ 720p; 120fps @ 1080p | Up to 240fps @ 1080p | |||||
| Time-lapse | Yes | ||||||
| 4K | 4K30 | 4K24, 4K30, 4K60 | |||||
| HDR | - | Yes | |||||
| Cinematic Mode | - | Yes | |||||
Other technologies

Apple has stack a few technologies on the iPhone to make the iPhone more capable and convenient over the generations. The iPhones are more aware with their surrounding with an integrated motion co-processor which have integrated accelerometer, gyroscopes and compasses. Now they are more aware with ultra-wide band sensors which can communicate with nearby compatible devices
Charging is also another area which the iPhone improves over generations. There’s always the lightning cable (which might go away pending EU’s directive). Then there are magnetic induction charging using the Qi standard makes it more convenient to charge the iPhone and later the MagSafe make it charge faster by properly aligning the magnetic coils perfectly through a series of magnets around the coils.
A smartphone now no longer is used just to take calls and send messages. It now can go to the internet to give and receive data from various servers from around the world. Cellular communications are now advanced that you can now stream multi-gigabit video right from your phone. Not only getting terrestrial service, but the iPhone can also get data from satellite that orbits the earth. What a time to be alive.
Battery is perhaps the most researched component in the smartphone after the screen and the camera. Since the widespread use of the smartphone, billions of dollars of R&D money has been poured into making better batteries so the devices will last longer and be more durable. Advances in chip manufacturing also makes new chip that is more energy efficiency while being more powerful. The iPhone 13 has the biggest battery that Apple makes and combine with the higher efficiency of the A15, it package a powerful punch of having a highly capable iPhone that can also last a long time.
| Feature | iPhone 6s Plus | iPhone 7 Plus | iPhone 8 Plus | iPhone Xr | iPhone 11 | iPhone 12 | iPhone 13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra sensors | ||||||||
| U1 Chip | - | Yes | ||||||
| Motion Co-processor | M9 | M10 (embedded with A10) | M11 (embedded with A11) | embedded | ||||
| Durability | ||||||||
| Screen Durability | Gorilla Glass | Apple Internal Glass | Ceramic Glass | |||||
| IP Rating | - | 67 | 68 | |||||
| Charging | ||||||||
| Fast Charging | No | Up to 10 W | Up to 20 W | |||||
| Qi Charging | - | Yes | ||||||
| Mag Safe | - | Yes | ||||||
| Connectivity | ||||||||
| Celluar connectivity | 4G | 5G | ||||||
| WiFi | Wifi 5 | Wifi 6 | ||||||
| Bluetooth | 4.2 | 5 | ||||||
| Battery | ||||||||
| Capacity (mAh) | 2750 | 2900 | 2691 | 2642 | 3110 | 2815 | 3240 | |
| Video Playback | Up to 14 hours | Up to 16 hours | Up to 17 hours | Up to 19 hours | ||||
| Video Playback (streamed) | - | Up to 10 hours | Up to 11 hours | Up to 15 hours | ||||
| Audio Playback | Up to 80 hours | Up to 60 hours | Up to 65 hours | Up to 75 hours | ||||
Conclusion
So while smartphones in general has reached a maturity level which does not warrants a yearly upgrade, but judging by how much technology advancements has been made over the years, you will find that that is is justifiable to upgrade your phone from 2 years ago and more so when you have an even older phone. So the take home message is this: You don’t need to upgrade your phone every year, so buy what you need at that moment and use it until you can’t. You will be rewarded on the next upgrade cycle which instead of a yearly, it’s a 2-3 years now, which you will see vast improvements.
Plug
Get your iPhone by following my Amazon affiliate links here:-
