Update: The Verge has reported that Apple delays the deployment of the CSAM detection feature after pushback from customers, advocacy groups and researchers.
Apple has marketed themselves over the years that they are a privacy first company. They have tried to built up a company image that Apple would never collect data about you, sell data about you to a 3rd party or track your usage throughout your online presence. In a world where the ads that you see on social network, Youtube and websites that you visit are especially tailored to you, and in some cases, in a creepy way, Apple selling point about privacy is well received.

However, that notion that Apple values your privacy has been put on to the test on August 2021 when Apple announced that in the next update of their software, they will implement a mechanism with the intention of protecting children. The first step is that it’s going to screen messages that your children receives (if they are using a device that is setup as a child account). The other step is they will use their user’s device to check illegal and disturbing images if the user decided to upload the photos to their platform. Apple swears that they are checking on contraband images in the most secure and private way.
However, backlash follows and a lot of groups started to scream at Apple as being a hypocrite. Some worries what else Apple will plan in the future and how the system will be jerry-rigged for nefarious purpose.
Now, after the dust has been settled, let’s explore what is Apple is actually doing and what are the stakeholders in this issue has to say about Apple next move.
What is CSAM

In the United States federal law defines child pornography as any visual depiction of sexually explicit conduct involving a minor (a person less than 18 years old). Child rights advocate would prefer to use the term CSAM - Child Sexual Abuse Material because it more accurately reflects the nature of the material - child being sexually abused and exploited. One of the major problems is when the files are being distributed on the internet, the child victim will suffer re-victimization whenever each time the images are viewed.
Apple, like any other platform companies, are taking steps to ensure that their platform is not being used to store and distribute such material. Apple was and is working with NCMEC - National Center for Missing & Exploited Children in the USA. NCMEC was founded bu the US Justice department although works independently of the Justice department. NCMEC does also work with other tech companies like Google, Facebook, Microsoft and others to combat child exploitation in the US.
In Apple’s case, NCMEC is where Apple gets information and source on CSAM images to test, validate and report on an exemplar. Other than Apple, other companies also get the same information from NCMEC about CSAM images.
Apple CSAM mechanism
Apple new feature to filter, detect and report CSAM presence in their platform does not have a catchy name at this point. However, they do have a dedicated page on how this feature work at the general level and since it has gotten a significant backlash, links to documents detailing the implementation and other security consideration.
From End Users Viewpoint
From end user viewpoint, the system works in two ways: First is to ensure child communication safety and the second is to detect, report and manage accounts that are holding any CSAM content.
For the first system, a system to screen communication to children, affect the Messages, Siri and Search app. This system will only work if the account is setup as a family account and the one who is receiving the message is designated as a child in that family account.
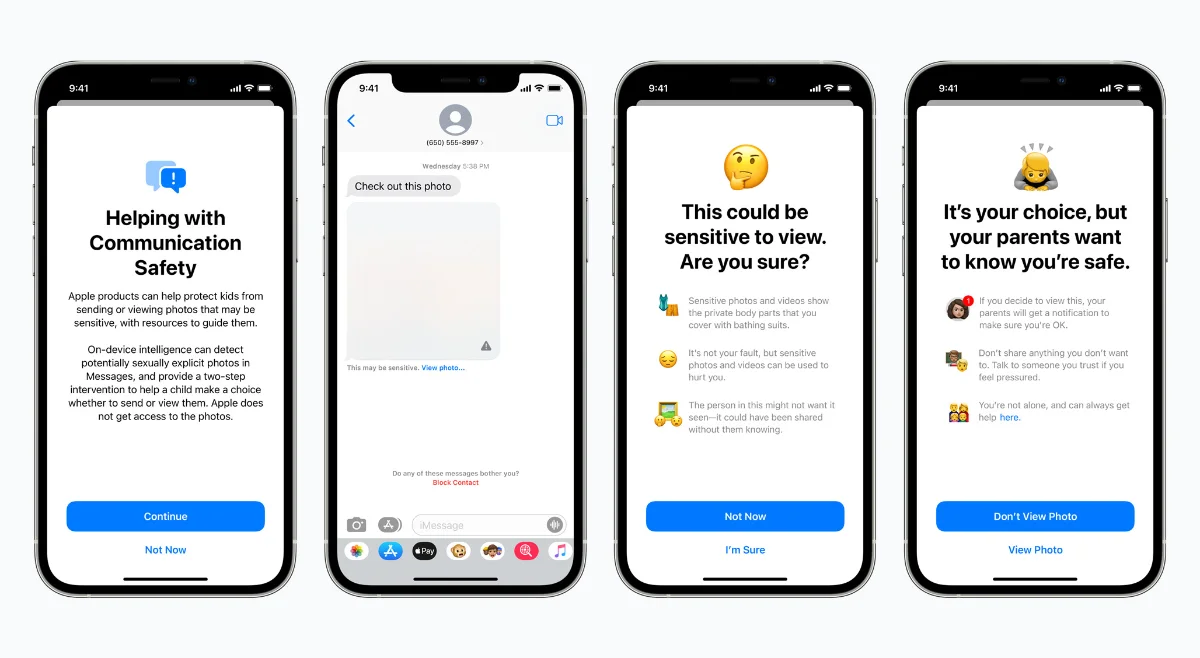
In messages, when the child account receive a notification that has been deemed as sexually explicit image. Apple claims that it will use machine learning technology to identify the image as sexually explicit. At this point, it’s unknown the effectiveness of Apple’s image recognition technology. So, when the child receive the content, the content will be blurred out first. If the child wants to view it, the content will be shown, but the parent will also be notified of such CSAM content reaching the child.
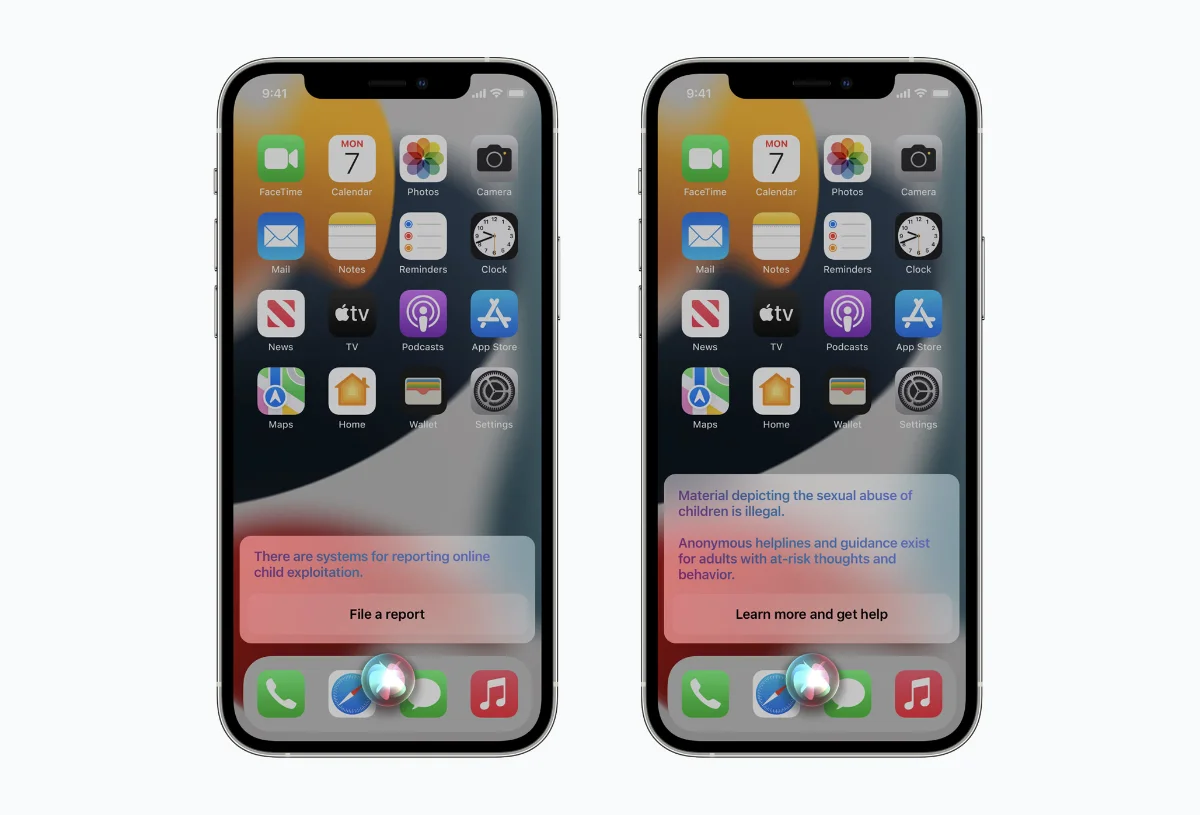
In Search and Siri, both apps will take a more protective approach to combat CSAM propagation and encounter. For example, when asked Siri about finding CSAM content, Siri will notify the user that such action is harmful and will point out resources and system to get help. Siri and Search will also help point out to system to report child exploitation if the user says the are in such situations.
The above is how Apple handled communication safety to children. The second part is how Apple handle CSAM content that is stored on their platform. From the user’s viewpoint, Apple will scan for CSAM content that you upload to Apple cloud services like iCloud storage and flagged your account if you holding CSAM content. Apple promises that the detection process will be private, it will be evaluated by a human and you have an avenue to appeal if you think you are wrongly accused for holding CSAM content.
Internals, as told by Apple
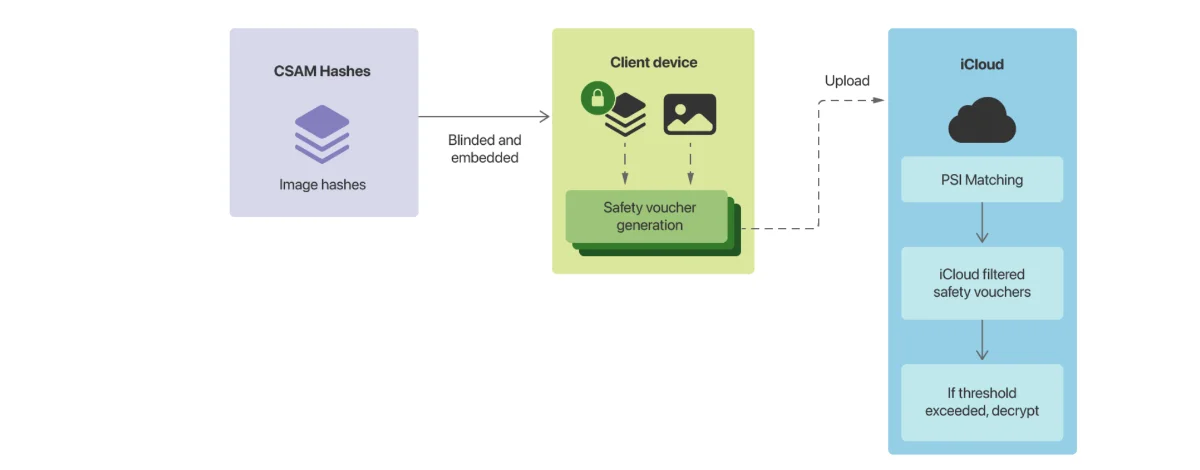
Now we have established how the entire process works from a user’s viewpoint, this is how the system works internally, as described by Apple. Since this comes from a technical document, there will be a lot of jargon flying around and I will try my best to explain the jargon in layman’s terms. The most important thing is to understand how the concept works.

Encryption - Is a method to change readable information into secret information by using mathematics. The simplest way to think of encryption is to use a chipper to translate an open information to a secret information. Why are we doing this is so from an outside perspective, the information looks like gibberish. And by using advanced mathematics, you can send encryption that is easy to decode if you have the key but hard to crack if you don’t.
Machine Learning - Often mistaken as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning or ML is a branch of Artificial Intelligence, which itself a branch of Computer Science. In supervised machine learning, the computer builds a model based on sample data and uses that model to make a prediction based on new set of data. Apple uses machine learning to classify images as sexualy explicit in messaging safety or matches to an image inside their CSAM database.
CSAM database - Now if you want to screen for CSAM contents in your platform, you need to know what you are looking for. In the case of Apple, Apple works with NCMEC to identify the CSAM materials that they are looking for. NCMEC maintains a database of known CSAM contents. Apple use this database to compare what are the users are uploading to their platform.

Hashing - In computer science, hashing is the process of transforming any given key or a string of characters into another value. One of the easiest way to think of hashing is to assign values to each letter of the alphabet - 1 for A and 26 for Z. So in the word, you convert each letter to a value and add them up. The sum is the hash. So HELLO will produce 52. Similar words like OLLEH will also produce the same hash value.

Neuralhash - This where things get interesting. Neuralhash is a technology developed by Apple to convert images into a hash value. What is unique about neuralhash that it is each picture that is wildly different will product a different hash value, but the pictures that are similar produce the same value. Similar in Apple terms is picture that might has change color, has change size or has been cropped slightly will produce the same value.
According to Apple, each CSAM image that was given by NCMEC has been assigned a unique Neuralhash value. According to Apple, when you upload your photos to their platform like iCloud photos, they will use your device to produce a Neuralhash on each of your uploaded images.
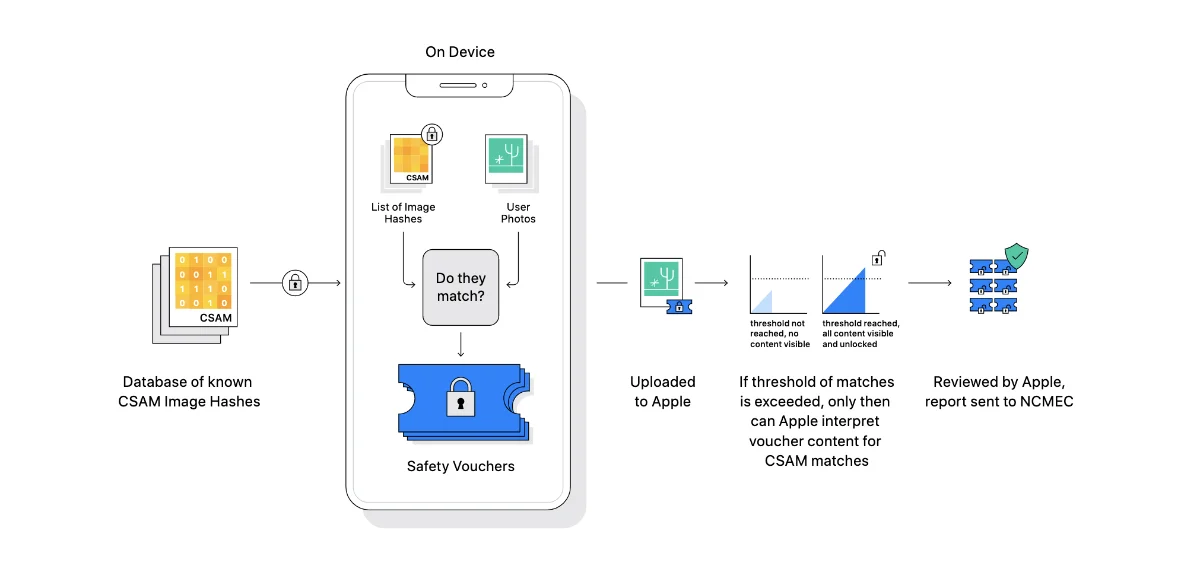
Private Set Intersection (PSI) - In the simplest term, PSI is Apple’s way to check if your images that you want to upload to iCloud is in the NCMEC database. A more detailed explanation that it uses encryption so that Apple does not know about any other images that you own, and Apple will only know about those images that you upload if you went above a threshold (which Apple won’t tell how high).
Threshold Secret Sharing (TSS) - TSS is Apple’s algorithm to ensure that Apple will only know if and only if you have enough CSAM content that warrants a red flag for Apple. Apple won’t tell how low or high the threshold will be
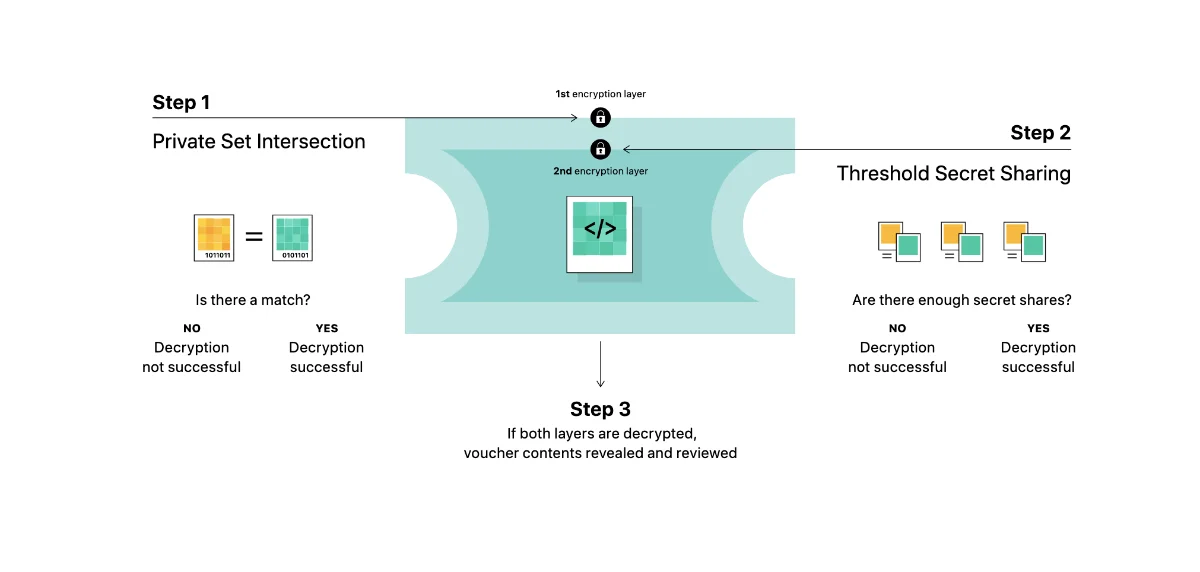
Safety Voucher - Safety Voucher is how Apple assign each picture that is uploaded to their platform like iCloud photos. Each image that is uploaded to iCloud (for example) will be assigned a Safety Voucher. A Safety Voucher is a double encryption device for each of your image. According to Apple, it can only be unlocked by Apple if the following two conditions are met: a) The Neuralhash of the image in question matches the one in CSAM database which is unlocked using the PSI method and b) there is enough images in your account, which is unlocked using the TSS method.
Conclusion In basic layman terms, Apple will encrypt all your photos that you sent to their platform. Each photos has two locks: An Image lock and a threshold lock. You need both locks to open to get your account to be red-flagged. The image lock will only unlock if your image matches the image that they have in their database. The threshold lock will only unlock if the number of images that you have breach their internal threshold. How they create the locks? They use your device to create the locks.
From Apple’s website, the detection system only looks for photos that you send or share on the iCloud platform, it will not affect photos that you put in your phone, it will only look for photos that are from the CSAM database that is supplied and maintained by NCMEC, and you need to hit a threshold before your account will be flagged. Apple decided to use users devices to digitally hash and encrypt the image instead of using their own servers.
What Apple Says About Child Safety
According to Apple, they want to detect and report CSAM image without compromising privacy and security. Through this method, Apple claims that they can reliably detect and flag accounts that hold CSAM contents at a significant threshold with out knowing about anything else that the user has.
On the privacy side, Apple claims that the feature will only be applied for photos that goes to their platform such as iCloud photos. It will not if the photos are private in their own devices. And the CSAM images will only be detected if the match in the CSAM database supplied by NCMEC.
In response to backlash, Apple has release documents explaining the technology that goes behind it. How the cryptography works in detecting offending images without knowing other images.
Apple promised that they will not adopt or modify the technology to detect non-CSAM images or bow under pressure from government (domestic or foreign) to modify the technology to detect non-CSAM images. Apple claims that the system is secure enough that non-CSAM images will not be injected into their database.
Criticism Against Apple
There are valid privacy concerns that are raised by rights group and also technology critics.
Firstly, nobody is against Apple checking for CSAM content in their own platform. The major concern is the manner which Apple is doing it. Instead of scanning for photos on their servers, they are using the user’s devices (iPhone, iPad and Mac) to tag each of the photos to be uploaded to their server. The concern if Apple is installing a backdoor to their own devices, which allow the to scan for other contents in the phone without the user’s knowledge. Apple vehemently denies such accusation.
Another concern if such technology, when implemented, allows Apple to setup the database to include non-CSAM images / content. This is a huge concern when Apple started to deploy the feature in more authorian governments that will try to pressure Apple to include non-CSAM images.
Center for Democracy & Technology (CDT) announced a letter with 90 other right groups in six continents raising concerns about he potential of the technology to “censor protected speech, threaten the privacy and security of people around the world, and have disastrous consequences for many children.”
Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) a leading digital rights group based in San Francisco raise concerns that such backdoor will used for nefarious purpose no matter how good the intentions are. They had said “Apple can explain at length how its technical implementation will preserve privacy and security in its proposed backdoor, but at the end of the day, even a thoroughly documented, carefully thought-out, and narrowly-scoped backdoor is still a backdoor.”
Apple can explain at length how its technical implementation will preserve privacy and security in its proposed backdoor, but at the end of the day, even a thoroughly documented, carefully thought-out, and narrowly-scoped backdoor is still a backdoor. - Electronic Frontier Foundation
Will Cathcart, head of Whatsapp on Facebook, criticize Apple implementation that Apple will scan all the photos that the user posses, even when that photo is not shared to anyone.
Apple’s own employees also raise concerns about the technology in their internal slack channel. One of the concerns is how the technology can be modified either by mandate or through hacking, to check for non-CSAM images in user phones.
Apple executives has reiterated several times, through the FAQs, through interviews with CNBC, Computeworld and also in an interview with Wall Street Journal, they will promise that the technology will not be used for nefarious purpose, they respect user privacy and they will not buckle by pressure from other governments to modify, alter or change the technology to track non-CSAM content.
What means for Apple and you in the future
So after all the back and forth between Apple and digital rights groups, what does it all mean to you? Firstly, no matter what, Apple has the moral obligation to ensure that their platform will not be use to distribute any CSAM images. So Apple will have to search and find out who is holding CSAM images in their platform.
Secondly, the method that Apple apply is very ground breaking and as far as I know, has not been done by any other tech company. Apple’s logic is to use cryptography and ML-powered hashing to look and detect CSAM images without actually knowing what’s inside your iCloud account. In other words, searching without looking. Using the user’s device to do the hard work of encrypting the photos is also a genius move because it help secure the information and reduces Apple workload to do it.
After all above being said, there is a legit concern that such technology might be use beyond it’s intended purpose. In an interview with Australian Financial Review, Tim Cook, the CEO of Apple, has mentioned that technology by itself is a neutral force. It’s the wielder who determined that the technology will be use for good or evil.
Yes, while Apple can believe it took the moral high ground, it does not mean that Apple does not bend to pressure especially by powerful authoritarian government. In China, Apple has turn iCloud data of Chinese users to a state-owned company. There is a longer debate about American values like freedom and liberty versus Chinese profits which help governments that totally oppose said American values. Digital rights group is not wrong to worry that the technology can and will be modified to monitor non-CSAM content in foreign countries that Apple operates in.
So, as of August 2021, it still up in the air if Apple will proceed with the implementation or fine-tune the implementation to better allay right groups concerns.
Bonus: What other cloud provider stance on CSAM.
Apple is not the first tech company that will scan their platform for CSAM content and they will definitely would not be the last to do it.
Alphabet Inc, the parent company of Google has tools for detecting and reporting CSAM content on their network and opens up the tool for anybody who is interested. They also work with NCMEC to scan, identify and flag accounts that is holding CSAM imagery.
Facebook with around 20 million reported incidents on their platform also has mechanism in place to find, scan and report accounts that hold and distribute CSAM images.
Amazon, through their Amazon Web Service hosting almost all of people website. They also sell storage online to 3rd party. They too have mechanism in place to find, scan and report accounts that hold and distribute CSAM images, especially an incident with SmugMug which uses their service.
